
Introduction
The demand for security and identity management for an organization or the customer has skyrocketed these recent years. All businesses hassle to satisfy the access demands and comply with the latest regulations. Every organization has a diverse landscape of users leveraging numerous devices with multiple network architecture and having disparate applications. Hence, managing such a complex security posture is difficult. If the organization fails to cater to sufficient identity and access security, the business might decline over time or may even damage its reputation. That is where Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions come to the rescue. IAMs are all in one toolkit to save the business and its prestige. This article will cater to broad details about what IAM is & its types, and how it benefits enterprises.
What is Identity and Access Management (IAM)?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a collective term that defines a framework or discipline of techniques, policies, rights, processes, and technology to manage digital identities. It is a state-of-the-art system that helps provide the right resource to the right individual as per their need. It fosters a company to set up privileges, roles, security policy, access control, and manage employee plus user identities. It also stays aligned with the different compliances such as GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 22301, FISMA, COPPA, ISO/IEC 27032, etc. Some widespread IAM vendors are SailPoint, Auth0, Cyberark, Okta, LoginRadius, ForgeRock, Saviynt, etc.
IAM functions as a centralized enterprise solution that can automate different types of authenticating and authorization within an organization. IAM enables network administrators and security professionals to monitor and supervise their employee access, network traffic, and manage privileges. It also defines how and to what extent employees and users can access various systems or other enterprise resources. Through IAM, corporate admins can set up to allow different authentications techniques. Most IAMs allow passwordless authentication, MFA, magic link, single sign-on (SSO), smart log-in, hardware-based authentication, etc. Also, it uses authentication protocols and systems like Security Access Markup Language (SAML), OpenID Connect (OIDC), and System for Cross-domain Identity Management (SCIM).
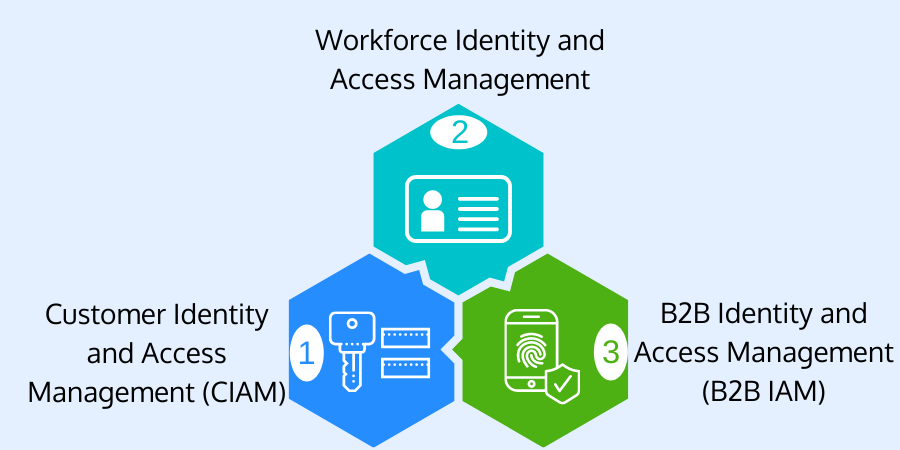
Types of IAM
IAM caters to a broad spectrum of users and customers like corporate employees, application end-users, business partners, etc. Based on the corporate requirements, enterprises leverage different types of IAMs. Here is a list of some popular IAM types.
1. Workforce Identity and Access Management: It is the traditional yet common type of IAM that every company leverages to manage and control electronic access and digital identity across the network. Companies either purchase IAM services from IAM providers or build them on-site, keeping in mind the security concerns taking help from CISOs and leading security professionals. Every organization will need a workforce IAM approach to cater to better security. It will help integrate authentication, authorization, and access policies with all disparate apps of the organization. Most of these IAMs also cater to features like risk-based authentication (RBA), federated authentication for employees, etc. Engaging a workforce enterprise-centric IAM will make the business stay aligned with all the latest compliances and security postures.
2. Customer Identity and Access Management (CIAM): CIAM is a branch of IAM that gets integrated with external applications such as social media apps, web apps, mobile apps, etc. They help in providing & setting access control and privileges to the application's digital properties. It permits the company to define how the app customers will access, authenticate, govern, use, and store data associated with the app. CIAM sits as an intermediary to render application security, customer experience, and analytics. CIAM enhances the end-user log-in experience by collecting details about customers & stores them in an encrypted data-rich identity profile system. Like stand IAMs, CIAMs also supports various authentication techniques like passwordless authentication, magic link, multi-factor authentication (MFA), single sign-on (SSO), smart log-in, hardware-based authentication, etc. Amazon, ForgeRock, LoginRadius, OneLogin, etc., are examples of CIAM solutions.
3. B2B Identity and Access Management (B2B IAM): B2B identity & access management solutions are specialized IAMs that cater to authentication & authorization for business clients with complex & extensive enterprise architecture. When businesses build custom IAM in-house, they often fail to deliver adequate security. It is because such IAMs require manual security updates. Also, such solutions struggle to scale when the company has to onboard numerous large business clients. That is why many companies switch to third-party IAM solutions that provide cloud-based IAM services (also called Identity-as-a-Service, IDaaS). It allows large enterprises with multiple business clients to employ IAM. B2B IAM also allows federated identity across multiple providers irrespective of any technology stack. Businesses usually purchase such third-party IAM services from IAM providers like Auth0, Cyberark, Okta, LoginRadius, ForgeRock, etc.

Importance of Identity and Access Management
For managing the overall electronic or digital identities of an enterprise and their authentication and authorization - IAMs are the best solutions. Every enterprise should leverage the benefits of IAM solutions. Even developing applications can use IAMs to make authentication more promising through dashboards. In this section, we will discuss the importance of IAM solutions.- Data Confidentiality: Securing the digital identity and preserving its confidentiality has become a grave concern. Data confidentiality is one of the fundamental pillars of cybersecurity. Data confidentiality determines that only the authorized party or individuals can modify the data. IAM protects data confidentiality by restricting particular users from accessing the enterprise's stored data, files, digital assets, and applications. Through IAMs, companies can competently secure sensitive data from external and internal bad actors.
- Minimize Human Error to a Significant Level: Often, it becomes difficult for the IT or the security team to manage the identity and access of on-boarding and off-boarding employees manually. Also, manually setting access privileges, group policies, and authorization mechanisms become a hectic task. That can also lead to human errors. Leveraging an IAM solution can help manage the entire enterprise's digital identity. It enables the enterprise to stop putting manual privileges & permissions for each employee account. Moreover, the IT and security team will not have to deal with irresponsible employees or accomplish tedious or repetitive tasks.
- Easy Maintenance of Regulatory Compliances: Every organization needs to follow certain industry-standard regulatory compliances like GDPR, SOC2, HIPAA, COPPA, ISO 22301, FISMA, etc. Leveraging an IAM helps the organization effectively implement and execute all compliances and does not require manual attention by the IT team. It ensures that the organization preserves the security and privacy of all users' or employees' digital identities.
- Proactive Threat Visibility and Mitigation: Data leakage and data breaches often damage the identity owner's confidence to use an application of a particular enterprise. Fortunately, IAMs come with robust enterprise-grade security through encryption for data at rest and data in transit. Also, it caters to a centralized service that provides proactive visibility to cyber threats and risk mitigation techniques to help secure enterprise assets and provide smooth authentication. Due to its centralized system, multiple departments and top-level executives can easily supervise the security postures and authorization ownerships.
- Effectual Ways of Accessing Enterprise Resources: Leveraging an IAM solution to cater to robust security for the entire enterprise assets helps manage a centralized system to access any resource. Also, through IAM, corporate employees can utilize different accessing mechanisms like single sign-on, biometric authentication, authentication through one-time links (magic links), hardware-based authentication (smart cards), and multi-factor authentication. Along with security postures, this also enhances the overall user experience. Through IAMs, the security team can limit the number of attempts employees can perform to authenticate themselves; hence, reducing the number of illicit attempts.
- Improves Work Productivity: Often, IAM security mechanisms come in between the employees to periodically check whether the authorized individual is leveraging the system or not. For that, IAMs pop up to authenticate employees, especially those working from home. Having authentication techniques like social login, biometric login, hardware-based authentication, magic link, or OTP-based logins help in quick login. It ultimately increases the productivity of all employees, and they do not have to remain stuck in authenticating themselves through long & cumbersome procedures. Also, such variations of authentication cater to the flexibility that employees can appreciate without irritation.
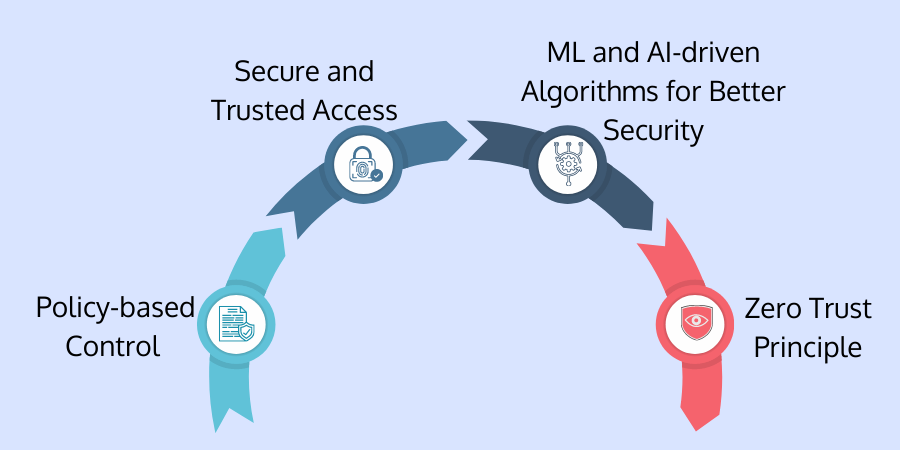
Various Security Strategies Used in IAM?
Zero-trust architecture is the cornerstone that IAM security implements at its core. Other than this security principle, there are numerous strategies we can implement through IAM.
- Policy-based Control: Companies can render the same privileges to employees through IAM by setting policies. No employees get excess authorization and right than is necessary. Since companies can manage the IAM solution centrally, top-level executives can monitor and confirm that only authorized persons access the resources, no matter from where they access them.
- Secure and Trusted Access: Since securing identity and employee access is the critical role of IAM, it assures that only the authorized person is accessing the resources. It uses strong encryption to protect employees' digital identities from identity theft and employee data breaches. It keeps logs of all authentication contexts such as time, location, device, etc.
- ML and AI-driven Algorithms for Better Security: IAM solutions also leverage Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to understand employees' behavior and other threats to stay ahead of such attacks. IAM also allows adaptive authentication and risk-based authentication. There it uses AI and ML to learn gradually through employee data. IAMs also use these technologies to detect external threats.
- Zero Trust Principle: The Zero Trust security principle depends on the policy of trusting no one and verifying each employee every time they do certain tasks or access specific enterprise resources. It is valid for individuals trying to access corporate resources from inside and outside the enterprise's network perimeter. Through the zero-trust principles, all access requests get scrutinized independently & affirmed before granting access to corporate resources.

 Batoi Corporate Office
Batoi Corporate Office